Posted on 10/17/13 by Courtney Smith
And here we are with part two of our rundown on the things you need to learn before you dive into the meaty stuff of A&P, specifically how to talk about the body. In our previous post, we discussed anatomical position and directional terms. In this post, we’re going to take a look at planes and cavities.


No, not the kind that fly you over oceans and have helpful people in uniforms that ply you with bags of stale peanuts. The other kind! The art kind, or in more technical terms the area of a two-dimensional surface. When used in conjunction with anatomy, planes are used to divide the body and its parts, which allows you to describe the views from which you study the body. If you look at your A&P textbook, you’ll most likely notice that a good number of the pictures and diagrams make use of planes.
Here is a list of commonly used planes:
|
Frontal (Coronal) plane |
Divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions |
|
Transverse plane |
Divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions |
|
Sagittal plane |
Vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sides. |
|
Midsagittal plane |
Divides the body at midline into equal right and left sides. |
|
Oblique plane |
Divides the body at an angle. |
Of course, in reality, the planes used are completely imaginary, but they are a helpful visual in terms of describing a view.
Want more information about anatomical planes? Check out our free Planes & Positions eBook!
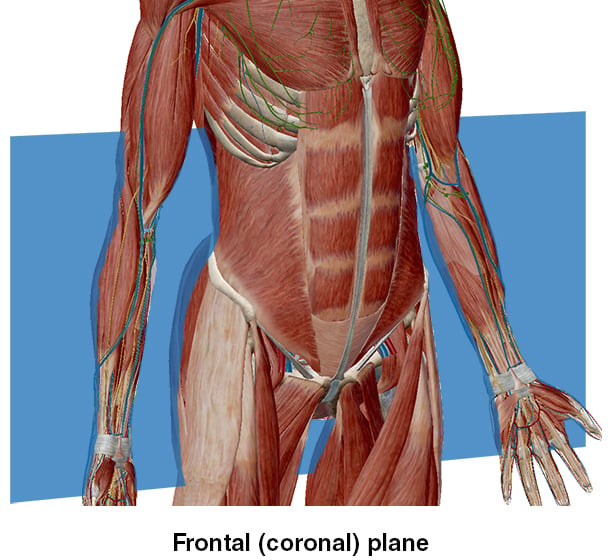
Using a frontal plane to bisect the body lengthwise, we’re able to describe certain areas that would not be easily visible or accessible if we used another plane.
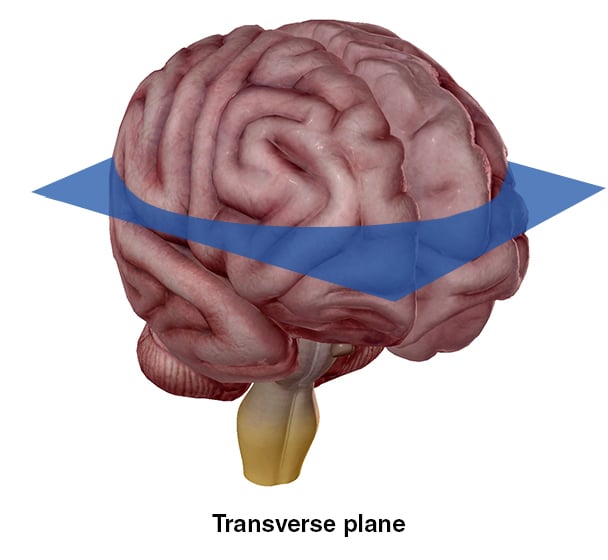
The transverse plane bisects the brain horizontally, allowing for a superior view.
Want a quick review of planes, positions, and directional terms? Check out this video:
A concept easier to grasp than planes and directional is body cavities, as they are a physical thing. When you hear the word “cavity,” no doubt you think of the kind in your teeth that are caused by plaque. A cavity, in any capacity, is a hollow place. In your teeth, it’s a hollow bit in the hard body. In the body itself, it is a hollow place usually filled with organs, nerves, vessels, and muscles.
Here are the body’s cavities:
|
Cranial cavity |
Formed by the cranial bones and holds the brain |
|
Vertebral canal |
Formed by the vertebrae and contains the spinal cord |
|
Thoracic cavity |
Formed by the thoracic cage, muscles of the chest, sternum, and the thoracic vertebrae; contains the pleural, pericardial, and mediastinum cavities |
|
Fluid-filled spaces that surround both lungs |
|
Fluid-filled space that surrounds the heart; the serous membrane of the pericardial cavity is the pericardium |
|
Central portion of the thoracic cavity; contains the heart, thymus, trachea, several major blood vessels, and esophagus |
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains liver, stomach, spleen, small intestine, and most of the large intestine; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is the peritoneum |
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains bladder, some of the large intestine, and reproductive organs (internal) |
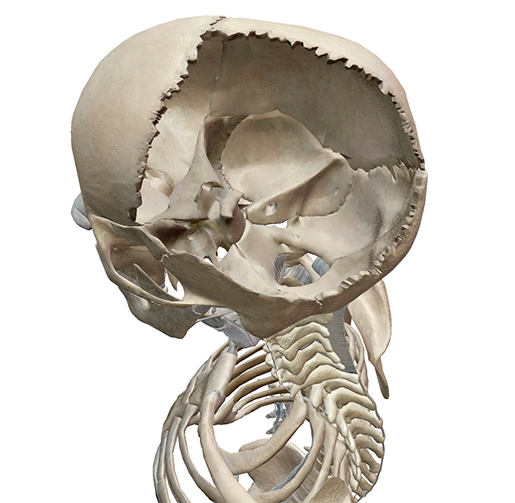 The cranial cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
The cranial cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
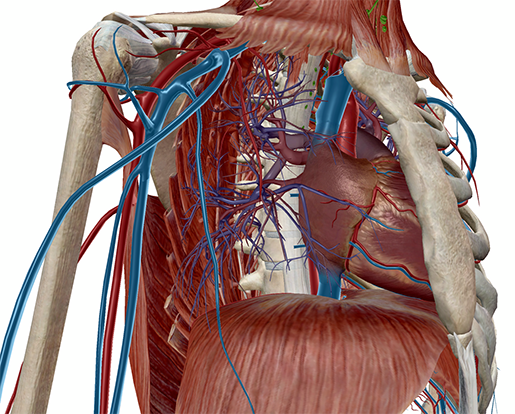 The thoracic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
The thoracic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
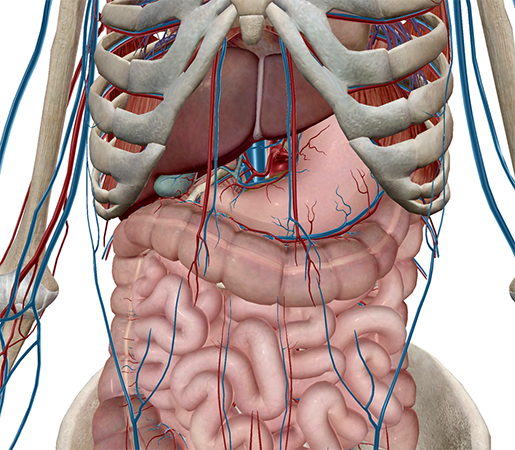 The abdominal cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
The abdominal cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
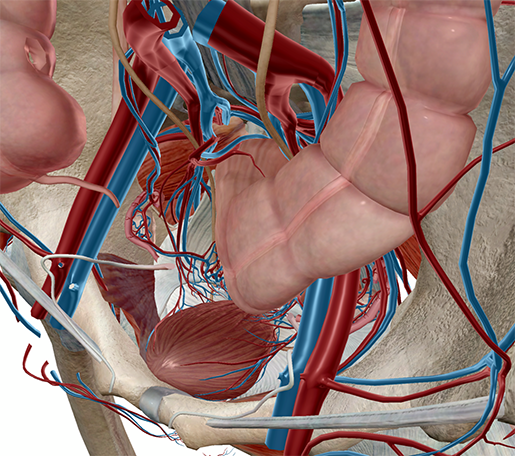 The pelvic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
The pelvic cavity. Image from Visible Body Suite.
VB Courseware, Visible Body's teaching and learning platform, comes packed with interactive 3D visual content and sophisticated course management tools that make it easy to teach planes, cavities, positions, and other basic terminology.
In addition to its library of 3D models, bite-sized learning modules, animations, histology slides, and simulations, Courseware contains a multitude of accessibility tools and features that ensure no student will be left behind. It also has a built-in gradebook that seamlessly integrates with learning management systems like Canvas, Blackboard, Moodle, and more.
To save instructors time and effort, Visible Body has designed premade, customizable curriculum content, including virtual labs and interactive 3D assignments that cover every body system as well as introductory biology topics.

See for yourself! You can get a free instructor trial of Courseware here.
Be sure to subscribe to the Visible Body Blog for more anatomy awesomeness!
Are you an instructor? We have award-winning 3D products and resources for your anatomy and physiology course! Learn more here.
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.
©2025 Visible Body, a division of Cengage Learning