3D Skeletal System: Function of the Sphenoid
Posted on 10/19/12 by Courtney Smith
The sphenoid.
Aside from having the most sci-fi name in all existence, it's pretty much the coolest-looking bone in the body. Best yet? It's in your skull. Bet you never thought you've been walking around all this time with a bat-shaped bone in your head.
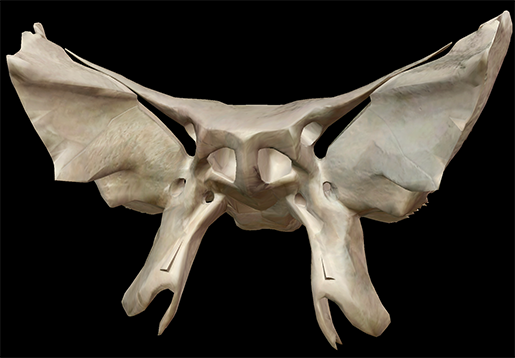
The sphenoid is an interesting bone in that while it doesn't actively protect the brain like the bones of the calvaria, it does have a multitude of functions, particularly in creating tunnels through which various nerves pass.
| Did you know? The sphenoid is an irregular bone. Check out the Learn Site to learn more about the five types of bones in the human body! |
Importance of the Sphenoid
There are 22 bones that make up the skull, and the sphenoid (don't you just love saying it?) is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium. It is situated at the base of the skull, acting as the keystone. A keystone in architecture is the piece at the apex of an arch; it locks all the other pieces together and bears the weight. And just like a keystone holds everything together in an archway, so does the sphenoid in the skull.
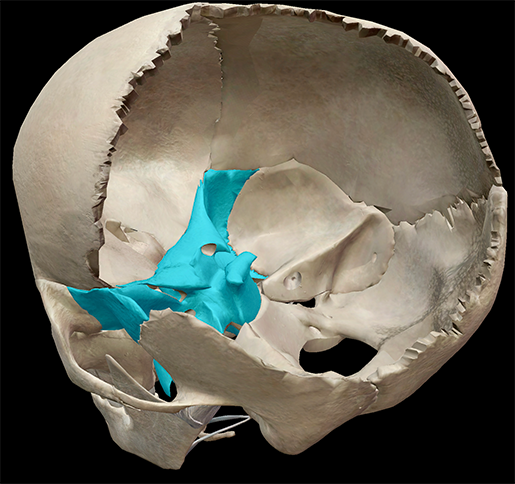 Image captured from Human Anatomy Atlas.
Image captured from Human Anatomy Atlas.
- frontal
- occipital
- parietals
- temporals
- zygomatics
- ethmoid
- vomer
- palatines
Of these 12 bones, 10 belong to the neurocranium. In my previous post, I discussed the neurocranium's role in protecting the brain. While it is part of the neurocranium, the sphenoid does little in the way of protection. It serves more as a base for the skull.
Sphenoid Landmarks
Our bat-shaped sphenoid is divided into a median body, two greater wings, two lesser wings, and two pterygoid plates.
Think of the body of the sphenoid as the body of the bat it's shaped like: it is from the body that the wings and processes project. It is cubical in shape. It also has two hollowed-out, air-filled cavities—the sphenoidal sinuses. There are four pairs of sinuses, and like the others the sphenoidal sinuses have two jobs: to help lighten the weight of the skull, and to give each person's voice individual character.
There is also a deep depression in the superior surface of the bone called the sella turcica, or "Turkish saddle." It is so named because of its resemblance to the saddles Turks used to use, with supports in the front and back. It is in this depression that the pituitary gland sits.
The greater and lesser wings are processes of bone that extend outward. The greater wings are perforated by various foramen, the most obvious being the large superior orbital fissures, which are formed by both sets of wings. Various structures pass through the fissures, including the oculomotor nerve (III); the trochlear nerve (IV); the lacrimal, frontal, and nasocillary branches of the ophthalmic nerve (V); and divisions of the ophthalmic vein. The greater wings also serve as the attachment site for the temporalis muscles.
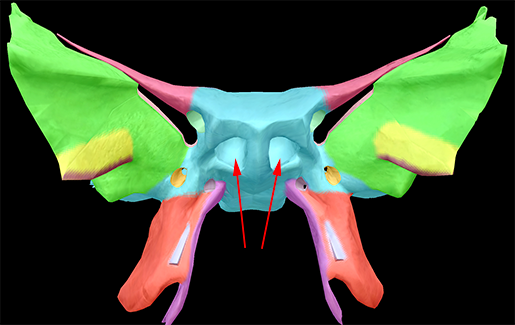 Image captured from Human Anatomy Atlas.
Image captured from Human Anatomy Atlas.
The lesser wings and the body of the sphenoid form the optic canal. It is through this canal that the optic nerve (II) passes from the brain to the eyes.
The lateral and medial processes project downward from the body of the bone, like legs. It is to the lateral processes that the lateral and medial pterygoid muscles attach. The sphenoidal processes of the palatine and the ala of the vomer articulate with the medial processes.
Pathologies of the Sphenoid
The thing about the sphenoid is that it's located in such a place that injuries to it are not as common as injuries to bones at the forefront of the skull. That said, you can definitely injure it. Fracturing the bone following severe bumps, impacts, and whiplash can affect vision or cause nerve damage.
One of the more common pathologies is sphenoid sinusitis. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of sinus cavities. Symptoms include headache, facial pain, and infected nasal drainage, as well as nerve irritation.
Sometimes, sinusitis can become very severe and complications, such as recesses (small cavities), can arise, or other issues can form in the sinuses (such as a tumor), prompting the need for a sphenoidotomy. A sphenoidotomy is, quite simply, the surgical procedure of cutting into the sphenoid sinus, with the most common approaches through the nasal cavity or nasal septum. A sphenoidectomy is when part of the sphenoid is removed, usually in instances involving tumors.
Hard to believe so much is associated with your bat bone, huh? The sphenoid, like all bones in the body, is a wellspring of information and serves a slew of purposes. Regardless of its importance, it is still—without a doubt—the coolest-looking bone you have.
Be sure to subscribe to the Visible Body Blog for more anatomy awesomeness!
Are you an instructor? We have award-winning 3D products and resources for your anatomy and physiology course! Learn more here.
Related Posts:
Additional Sources:
- Rimal, D., Hashmi, S., & Prinsley, P. (2006). An unusual presentation of sphenoid sinusitis with septicaemia in a healthy young adult. Emergency Medicine Journal, 23(36), doi: 10.1136/emj.2005.033340
- Schaefer, MD, S. (2012). Sphenoidotomy. In Retrieved from http://www.nyee.edu/ent_rss_sts_sphenoid01.html



